This module is designed for Venturing and Sea Scouts to explore how science affects your life each day.
Launch!
Requirements last updated 2022-05-25. There are broken links and outdated information in places and formatting may not match between two Nova awards because the requirements are preserved to match the original state from Scouting America. Where available, the related counselor notes have been included along with the requirements.
1.
Choose A or B or C and complete ALL the requirements.
A.
Watch about three hours total of science-related shows or
documentaries that involve projectiles, aviation, weather,
astronomy, or space technology. Then do the following:
1.
Make a list of at least two questions or ideas from each
show.
2.
Discuss two of the questions or ideas with your counselor.
Some examples include - but are not limited to - shows found on
PBS ("NOVA"), Discovery Channel, Science Channel, National
Geographic Channel, TED Talks (online videos), and the
History Channel. The NASA website at www.nasa.gov has some
short multimedia clips that involve projectiles, aviation,
space, weather, astronomy, or aviation or space technology.
You may choose to watch a live performance or movie at a
planetarium or science museum instead of watching a media
production. You may watch online productions with your
counselor's approval and under your parent's supervision.
B.
Read (about three hours total) about projectiles, aviation, space,
weather, astronomy, or aviation or space technology. Then do the
following:
1.
Make a list of at least two questions or ideas from each
article.
2.
Discuss two of the questions or ideas with your counselor.
Examples of magazines include - but are not limited to - Odyssey,
Popular Mechanics, Popular Science, Science Illustrated,
Discover, Air & Space, Aviation Week, Astronomy, Science
News, Natural History, Robot, Servo, and Scientific American.
C.
Do a combination of reading and watching (about three hours total).
Then do the following:
1.
Make a list of at least two questions or ideas from each
article or show.
2.
Discuss two of the questions or ideas with your counselor.
2.
Choose ONE STEM field of interest from the following list. Complete ALL
the requirements for a STEM exploration in that field. See STEM
Explorations for the requirements. (If you have
already completed a Venturing or Sea Scouts STEM exploration in one of
these fields, you must choose a different field for this award.)
Archery, Astronomy, Aviation, Digital Technology, Rifle Shooting,
Robotics, Shotgun Shooting, Space Exploration, Weather
3.
Choose A or B and complete ALL the requirements.
A.
Simulations. Find and use a projectile simulation applet on the
Internet (with your parent's or guardian's permission). Then design
and complete a hands-on experiment to demonstrate projectile
motion.
1.
Keep a record of the angle, time, and distance.
2.
Graph the results of your experiment. (Note: Using a
high-speed camera or video camera may make the graphing
easier, as will doing many repetitions using variable heights
from which the projectile can be launched.)
Helpful Links
Be sure you have your parent's or guardian's permission
before using the Internet. Some of these websites
require the use of Java runtime environments. If your
computer does not support this program, you may not be
able to visit those sites.
Projectile Motion Applets
Website: http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/Applets/Projectile/projectile.html Fowler's Physics Applets
Website: https://www.compadre.org/introphys/items/detail.cfm?ID=7823 Java Applets on Physics
Website: https://www.cco.caltech.edu/~phys1/java.html
Website: http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/Applets/Projectile/projectile.html Fowler's Physics Applets
Website: https://www.compadre.org/introphys/items/detail.cfm?ID=7823 Java Applets on Physics
Website: https://www.cco.caltech.edu/~phys1/java.html
3.
Discuss with your counselor:
a.
What a projectile is
A projectile is:
- An object that is fired, launched, or thrown, but which cannot propel itself
- A self-propelled missile, like a rocket
b.
What projectile motion is
c.
The factors affecting the path of a projectile
When an object is fired, launched, or thrown, it
is given horizontal velocity. (Velocity is the
same as speed, but it is speed in a given
direction.) Once the object is launched, no
additional force providing horizontal velocity is
applied. Newton's First Law of Motion states that
a body at rest stays at rest and a body in motion
stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside
force. If gravity did not act on the projectile's
path, the object would continue to move in the
direction in which it was launched. Once the
object has been launched, the only force acting
upon it is the force of gravity, which
accelerates the object toward Earth.
Projectile motion is the curved path taken by an
object that is fired, launched, or thrown.
Helpful Links
"Free Fall and the Acceleration of Gravity": The Physics Classroom
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l5b.cfm "Vectors - Fundamentals and Operations": The Physics Classroom
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/u3l1e.cfm#trig "Projectile Motion": The Physics Classroom
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/u3l2a.cfm Projectile motion is caused by the force of gravity giving vertical acceleration to an object that has horizontal velocity. (When an object is thrown straight up in the air, the force of gravity slows it down, it comes momentarily to a complete stop, then it accelerates downward.) An object that has been launched will continue to move in the direction it was thrown at the speed with which it was thrown, except for being slowed down by friction with the air (air resistance), but it will begin to accelerate toward Earth, moving faster toward Earth all the time. The combination of constant horizontal velocity and increasing downward velocity due to the acceleration of gravity is what gives a projectile its curved path.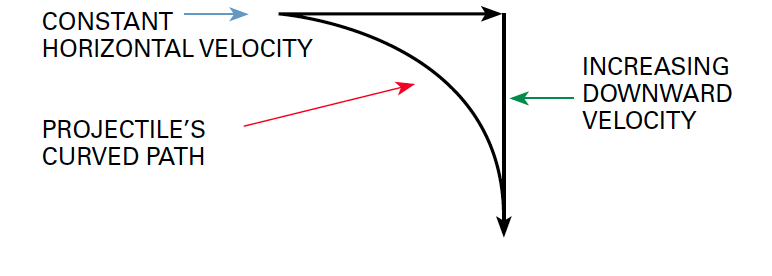 Forward velocity is the speed horizontal to Earth
given to a projectile. If the projectile is
thrown parallel to Earth, all of its original
speed will be its forward velocity. If an object
is thrown at an angle to Earth, the forward
velocity is that portion of the velocity that is
parallel to Earth.
(Determining forward velocity can be done by
separating the velocity into horizontal and
vertical components - like on a triangle - using
vector resolution.)
Forward velocity has a constant speed.
Acceleration due to gravity slows down things
that are moving upward and speeds up things that
are moving downward. At most locations on Earth,
the acceleration of gravity (9.80 m/s², or
~32.174 ft/s²) will cause an object to fall 9.8
meters per second faster each second. An object
starting with no vertical motion will be falling
toward Earth at the rate of 9.8 m/s at the end of
one second and at the rate of 19.6 m/s at the end
of two seconds. Acceleration due to gravity is
constantly changing the vertical speed / velocity
of an object.
Forward velocity is the speed horizontal to Earth
given to a projectile. If the projectile is
thrown parallel to Earth, all of its original
speed will be its forward velocity. If an object
is thrown at an angle to Earth, the forward
velocity is that portion of the velocity that is
parallel to Earth.
(Determining forward velocity can be done by
separating the velocity into horizontal and
vertical components - like on a triangle - using
vector resolution.)
Forward velocity has a constant speed.
Acceleration due to gravity slows down things
that are moving upward and speeds up things that
are moving downward. At most locations on Earth,
the acceleration of gravity (9.80 m/s², or
~32.174 ft/s²) will cause an object to fall 9.8
meters per second faster each second. An object
starting with no vertical motion will be falling
toward Earth at the rate of 9.8 m/s at the end of
one second and at the rate of 19.6 m/s at the end
of two seconds. Acceleration due to gravity is
constantly changing the vertical speed / velocity
of an object.
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1dkin/u1l5b.cfm "Vectors - Fundamentals and Operations": The Physics Classroom
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/u3l1e.cfm#trig "Projectile Motion": The Physics Classroom
Website: https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/vectors/u3l2a.cfm Projectile motion is caused by the force of gravity giving vertical acceleration to an object that has horizontal velocity. (When an object is thrown straight up in the air, the force of gravity slows it down, it comes momentarily to a complete stop, then it accelerates downward.) An object that has been launched will continue to move in the direction it was thrown at the speed with which it was thrown, except for being slowed down by friction with the air (air resistance), but it will begin to accelerate toward Earth, moving faster toward Earth all the time. The combination of constant horizontal velocity and increasing downward velocity due to the acceleration of gravity is what gives a projectile its curved path.
 Forward velocity is the speed horizontal to Earth
given to a projectile. If the projectile is
thrown parallel to Earth, all of its original
speed will be its forward velocity. If an object
is thrown at an angle to Earth, the forward
velocity is that portion of the velocity that is
parallel to Earth.
(Determining forward velocity can be done by
separating the velocity into horizontal and
vertical components - like on a triangle - using
vector resolution.)
Forward velocity has a constant speed.
Acceleration due to gravity slows down things
that are moving upward and speeds up things that
are moving downward. At most locations on Earth,
the acceleration of gravity (9.80 m/s², or
~32.174 ft/s²) will cause an object to fall 9.8
meters per second faster each second. An object
starting with no vertical motion will be falling
toward Earth at the rate of 9.8 m/s at the end of
one second and at the rate of 19.6 m/s at the end
of two seconds. Acceleration due to gravity is
constantly changing the vertical speed / velocity
of an object.
Forward velocity is the speed horizontal to Earth
given to a projectile. If the projectile is
thrown parallel to Earth, all of its original
speed will be its forward velocity. If an object
is thrown at an angle to Earth, the forward
velocity is that portion of the velocity that is
parallel to Earth.
(Determining forward velocity can be done by
separating the velocity into horizontal and
vertical components - like on a triangle - using
vector resolution.)
Forward velocity has a constant speed.
Acceleration due to gravity slows down things
that are moving upward and speeds up things that
are moving downward. At most locations on Earth,
the acceleration of gravity (9.80 m/s², or
~32.174 ft/s²) will cause an object to fall 9.8
meters per second faster each second. An object
starting with no vertical motion will be falling
toward Earth at the rate of 9.8 m/s at the end of
one second and at the rate of 19.6 m/s at the end
of two seconds. Acceleration due to gravity is
constantly changing the vertical speed / velocity
of an object.d.
The difference between forward velocity and
acceleration due to gravity
B.
Discover. Explain to your counselor the difference between escape
velocity (not the game), orbital velocity, and terminal velocity.
Then answer TWO of the following questions. (With your parent's or
guardian's permission, you may explore websites to find this
information.)
1.
Why are satellites usually launched toward the east, and what
is a launch window?
Escape velocity is the speed at which an object will be
able to escape the gravity of Earth, the moon, or other
body. An object must travel fast enough that it will
not fall back to the surface. Escape velocity from
Earth is 11.2 km/s, or 25038.72 mph. Escape velocity is
proportional to the square root of the ratio between
the mass of the larger body and the distance of the
smaller object from the center of the larger body.
Helpful Links
"Escape Velocity": Georgia State University
Website: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/vesc.html Orbital velocity is achieved when an object's horizontal velocity balances the acceleration of gravity at that location in space. An object that has orbital velocity (is in orbit) continues to fall toward Earth as it travels away from Earth, giving the object a circular path around Earth. The object continually falls around Earth due to the combination of horizontal velocity and acceleration due to gravity. Terminal velocity is the point at which the acceleration of gravity on an object matches the air resistance of the object. Terminal velocity is affected by the weight of the object and its orientation. (The more surface area that is horizontal to Earth, the lower the terminal velocity. Skydivers who perform aerial displays use this fact. The first divers to jump lie flat to increase their air resistance. Later divers streamline dive by holding their arms and legs tightly to their bodies and dive headfirst toward Earth in order to catch the earlier divers in the air.) Note: If it were not for air resistance, all objects, regardless of mass, size, or any other factor, would fall at the SAME velocity. Watch astronauts David Scott and Jim Irwin do Galileo's experiment on the moon. "David Scott does the feather hammer experiment on the moon"
Video: https://youtu.be/Oo8TaPVsn9Y When satellites are launched to the east, Earth's spin effectively adds to their velocity, making escape velocity easier to obtain and requiring less fuel. Not all spacecraft are launched toward the east; the launch direction depends also on the final orbit and purpose of the satellite. In order for a spacecraft to rendezvous with another spacecraft or other object in space, the orbits of both objects must be taken into consideration. A launch window describes a time period in which a mission must be launched for the objects' orbits to overlap.
Website: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/vesc.html Orbital velocity is achieved when an object's horizontal velocity balances the acceleration of gravity at that location in space. An object that has orbital velocity (is in orbit) continues to fall toward Earth as it travels away from Earth, giving the object a circular path around Earth. The object continually falls around Earth due to the combination of horizontal velocity and acceleration due to gravity. Terminal velocity is the point at which the acceleration of gravity on an object matches the air resistance of the object. Terminal velocity is affected by the weight of the object and its orientation. (The more surface area that is horizontal to Earth, the lower the terminal velocity. Skydivers who perform aerial displays use this fact. The first divers to jump lie flat to increase their air resistance. Later divers streamline dive by holding their arms and legs tightly to their bodies and dive headfirst toward Earth in order to catch the earlier divers in the air.) Note: If it were not for air resistance, all objects, regardless of mass, size, or any other factor, would fall at the SAME velocity. Watch astronauts David Scott and Jim Irwin do Galileo's experiment on the moon. "David Scott does the feather hammer experiment on the moon"
Video: https://youtu.be/Oo8TaPVsn9Y When satellites are launched to the east, Earth's spin effectively adds to their velocity, making escape velocity easier to obtain and requiring less fuel. Not all spacecraft are launched toward the east; the launch direction depends also on the final orbit and purpose of the satellite. In order for a spacecraft to rendezvous with another spacecraft or other object in space, the orbits of both objects must be taken into consideration. A launch window describes a time period in which a mission must be launched for the objects' orbits to overlap.
2.
What is the average terminal velocity of a skydiver? (What is
the fastest you would go if you were to jump out of an
airplane?)
Terminal velocity is when the acceleration due to
gravity is matched by the air resistance (or resistance
of whatever fluid the object is traveling through).
When the acceleration of gravity is balanced by air
resistance, the object continues to fall, but it does
not increase its velocity.
"A person has a terminal velocity of about 200 mph when
balled up and about 125 mph with arms and feet fully
extended to catch the wind." Source: "Speed of a
Skydiver (Terminal Velocity)," The Physics Factbook,
website https://hypertextbook.com/facts/1998/JianHuang.shtml.
3.
How fast does a bullet, baseball, airplane, or rocket have to
travel in order to escape Earth's gravitational field? (What
is Earth's escape velocity?)
Helpful Links
"Orbital Mechanics": Rocket & Space Technology
Website: http://www.braeunig.us/space/orbmech.htm "What is a 'launch window'?": ESA
Website: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/What_is_a_launch_window "Launch Windows: How NASA Decides When to Fly": NRP
Website: https://www.npr.org/2005/07/25/4749663/launch-windows-how-nasa-decides-when-to-fly "Terminal Velocity": NASA
Website: https://www1.grc.nasa.gov/beginners-guide-to-aeronautics/termvel/ Escape velocity from Earth is 11.2 km/s, or 25038.72 mph.
Website: http://www.braeunig.us/space/orbmech.htm "What is a 'launch window'?": ESA
Website: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/What_is_a_launch_window "Launch Windows: How NASA Decides When to Fly": NRP
Website: https://www.npr.org/2005/07/25/4749663/launch-windows-how-nasa-decides-when-to-fly "Terminal Velocity": NASA
Website: https://www1.grc.nasa.gov/beginners-guide-to-aeronautics/termvel/ Escape velocity from Earth is 11.2 km/s, or 25038.72 mph.
4.
Choose A or B and complete ALL the requirements.
A.
Visit an observatory or a flight, aviation, or space museum.
1.
During your visit, talk to a docent or person in charge about
a science topic related to the site.
2.
Discuss your visit with your counselor.
B.
Discover the latitude and longitude coordinates of your current
position. Then do the following:
1.
Find out what time a satellite will pass over your area. (A
good resource to find the times for satellite passes is the
Heavens Above website at https://www.heavens-above.com/)
2.
Watch the satellite using binoculars. Record the time of your
viewing, the weather conditions, how long the satellite was
visible, and the path of the satellite. Then discuss your
viewing with your counselor.
5.
Choose A or B or C and complete ALL the requirements.
A.
Design and build a catapult that will launch a marshmallow 4 feet.
Then do the following:
1.
Keep track of your experimental data for every attempt.
Include the angle of launch and the distance projected.
2.
Make sure you apply the same force every time, perhaps by
using a weight to launch the marshmallow.
Discuss your design, data, and experiments - both successes and
failures - with your counselor.
B.
Design a pitching machine that will lob a softball into the strike
zone. Answer the following questions, then discuss your design,
data, and experiments - both successes and failures - with your
counselor.
1.
At what angle and velocity will your machine need to eject
the softball in order for the ball to travel through the
strike zone from the pitcher's mound?
2.
How much force will you need to apply to power the ball to
the plate?
3.
If you were to use a power supply for your machine, what
power source would you choose and why?
C.
Design and build a marble run or roller coaster that includes an
empty space where the marble has to jump from one part of the chute
to the other. Do the following, then discuss your design, data, and
experiments - both successes and failures - with your counselor.
1.
Keep track of your experimental data for every attempt.
Include the vertical angle between the two parts of the chute
and the horizontal distance between the two parts of the
chute.
2.
Experiment with different starting heights for the marble.
How do the starting heights affect the velocity of the
marble? How does the starting height affect the jump
distance?
6.
Discuss with your counselor how science affects your everyday life.

